Tuesday 7th October 2025
CO (carbon monoxide) is extremely dangerous even at low levels (50ppm+) and comes from incomplete combustion. CO2 (carbon dioxide) is naturally occurring and only dangerous at very high levels (800ppm+ indoors). Both are colourless and odourless. You need a CO detector for safety; CO2 monitors help with air quality. CO can kill quickly; CO2 mainly affects comfort and concentration at typical indoor levels.
Do you know the difference between carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide? These two gases might sound similar, but understanding what is the difference between them could literally save your life. Both are invisible threats lurking in our homes, offices and public spaces yet they pose completely different risks and require different detection methods.
Carbon monoxide vs carbon dioxide: what’s the difference?
[Keep existing chemical structure diagram]
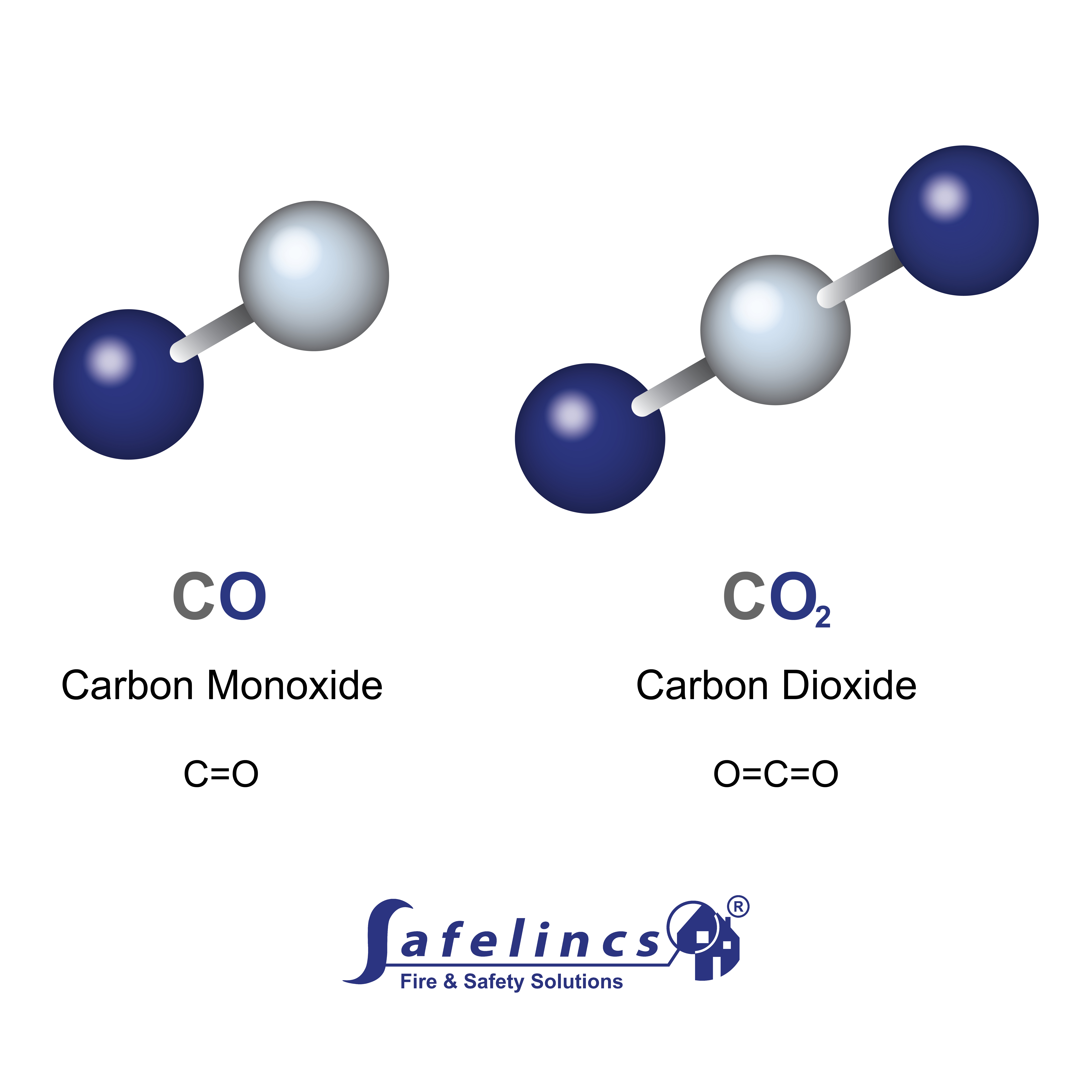
CO and CO2 are both colourless, odourless gases. However, they’re chemically different: CO is one oxygen atom bound to one carbon atom, whereas CO2 is two oxygen atoms bound to one carbon atom. This difference in CO vs CO2 bond length and molecular structure makes all the difference when it comes to their effects on human health.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) vs carbon monoxide (CO) represents a crucial distinction every homeowner should understand. CO2 is a product of many natural processes in the human body and is safe at normal levels. Due to the similarity in their chemical structure, however, CO is a dangerous gas that’s toxic even at low levels.
What is CO?
Carbon Monoxide is released during ‘incomplete combustion’. This usually happens when a fuel, such as coal, wood or oil, is burned without enough oxygen present. This deadly gas is dangerous even at very low levels. Because its molecules are very similar in structure to CO2, they bind to red blood cells in the body and become ‘stuck’. As a result, the amount of oxygen that can be transported to the body’s essential organs is reduced. This lack of oxygen can cause fatigue, breathlessness, headaches and eventually death.
Levels as low as 50ppm (parts per million) will cause harm, particularly with prolonged exposure, whereas 700ppm can quickly be fatal.
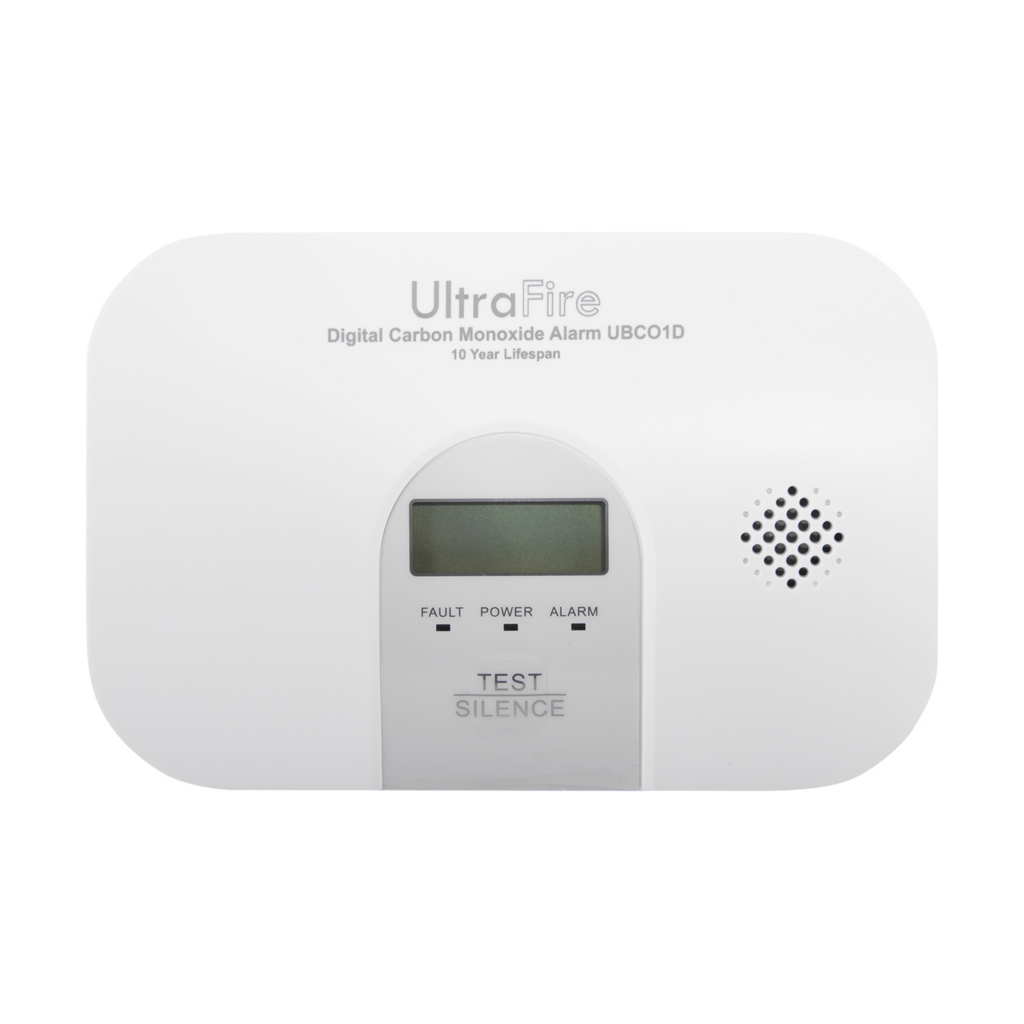
Any level of CO therefore warrants concern, which can only be detected with a working CO detector.
What is CO2?
Carbon Dioxide is released by many natural chemical processes, including combustion, respiration and decomposition. CO2 is used to give fizzy drinks their bubbles, and as a medium in some fire extinguishers. It’s also present in the air we breathe, where it’s safe at normal levels (under 800ppm). However, at extreme levels, CO2 can cause asphyxiation by reducing the level of oxygen available.

CO vs CO2 symptoms
Both CO and CO2 can cause headaches, but the similarities end there. CO vs CO2 symptoms vary significantly:
CO symptoms include:
- Headaches and dizziness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fatigue and weakness
- Chest pain
- Confusion
CO2 symptoms at high levels include:
- Drowsiness
- Headaches
- Increased heart rate
- Mild narcosis
CO vs CO2 smell
Here’s a crucial point about CO vs CO2 smell: neither gas has any detectable odour. You cannot smell either carbon monoxide or carbon dioxide, which makes them particularly dangerous. This is why detection equipment is absolutely essential.
CO or CO2, which is more dangerous?
Carbon monoxide vs carbon dioxide: let’s compare their danger levels. CO is significantly more dangerous at lower concentrations. Carbon monoxide can be lethal at just 700ppm, whereas CO2 becomes dangerous only at much higher concentrations (around 40,000ppm for immediate danger).
CO2 and indoor air quality
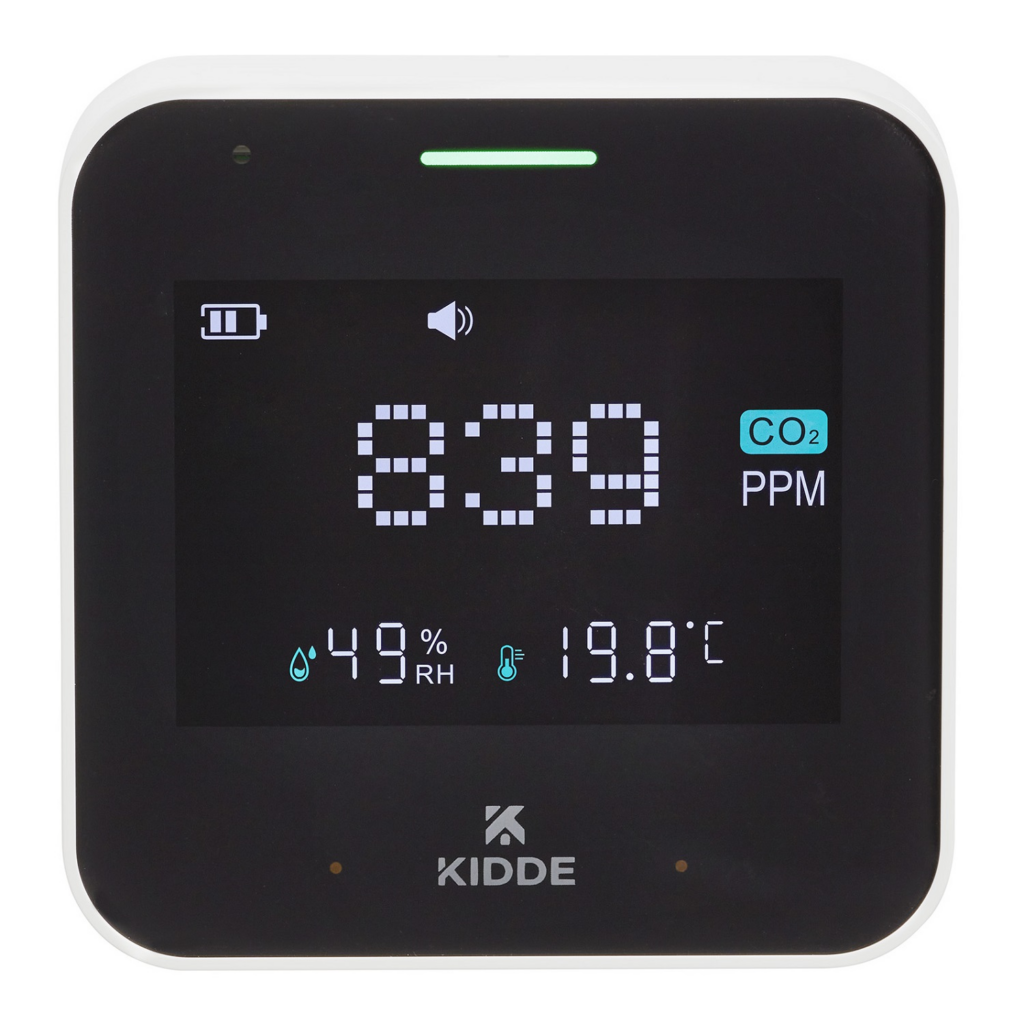
Although carbon dioxide is naturally present in the air, high levels can have negative effects on human health. Poor ventilation in an enclosed environment can lead to raised CO2 levels. This often leads to headaches, fatigue and poor concentration. Safe indoor levels are below 800ppm; in classrooms, offices and other public venues, levels can easily reach over 1000ppm.You can improve indoor air quality by opening windows to improve ventilation, installing air purifiers, and reducing damp and humidity with dehumidifiers. Measuring CO2 levels with an indoor air quality monitor is the best way to track this and know when improvements must be made.
Do I need a carbon monoxide or dioxide detector?
This question arises frequently, and the answer depends on your situation. CO and CO2 detector needs vary:
CO detectors should be installed to detect the presence of CO. Without this, it’s impossible to detect the presence of this deadly gas, which is dangerous even at low levels. A CO alarm with a digital display allows users to monitor levels too low to trigger the alarm, encouraging them to improve ventilation.
CO and CO2 monitor systems have traditionally been used in commercial premises like breweries or laboratories, where fatal levels of CO2 might be released by chemical reactions. However, new technology has made these detectors more affordable and accessible. CO and CO2 sensor technology is now recommended in schools, offices and even homes to track and improve indoor air quality.
Will CO2 set off a CO detector?
No, CO2 will not set off a CO detector. These devices use different sensing technologies. A CO vs CO2 detector comparison shows they’re designed for completely different gases. CO vs CO2 sensor technology works on different principles, so you need the right detector for the right gas.
Detecting CO vs CO2
CO and CO2 detector installation requires different approaches. Carbon monoxide detectors should be installed to detect the presence of CO, whereas CO vs CO2 sensor systems for carbon dioxide monitoring focus on air quality management.
CO detector technology typically uses electrochemical sensors, whereas CO and CO2 sensor systems for carbon dioxide often use infrared technology. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right protection for your home.
Glossary of Terms
Carbon monoxide (CO): A toxic gas with one carbon atom and one oxygen atom, produced by incomplete combustion
Carbon dioxide (CO2): A natural gas with one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms, produced by respiration and combustion
ppm: Parts per million – a measurement of gas concentration
Incomplete combustion: Burning fuel without sufficient oxygen, producing dangerous CO
Electrochemical sensor: Technology used in CO detectors to identify carbon monoxide
Infrared sensor: Technology commonly used in CO2 monitors
Asphyxiation: Suffocation caused by a lack of oxygen
Indoor Air Quality (IAQ): The air quality within buildings, affected by CO2 levels, among other factors
CO vs CO2: both are colourless, odourless gases, which pose different health risks. The only way to stay safe from these gases is to have the appropriate detector fitted. For additional support in selecting the best detector for your needs, contact our friendly customer support team on 0800 612 6537.
All information is correct at the time of posting.