Thursday 2nd May 2024
What is a fire exit?
The final exits on escape routes in public buildings are known as fire exits. These doors should open easily and immediately. Wherever practicable, they should open “in the direction of escape”, i.e., outwards into a place of safety outside the building. Push pads and panic bars are often fitted on fire exits to ensure this.
Sometimes fire exit doors are, under normal circumstances, part of the usual route of traffic, such as a front door. Fire exits can also be for emergency use only, and not used during normal operation. Sliding or revolving doors must not be used for exits specifically intended as fire exits.
Emergency routes and fire exits must be well lit, and indicated by appropriate signs, e.g. “Fire Exit – Keep Clear”. In locations that require illumination, emergency lighting of adequate intensity must be provided. This ensures that if the normal lighting fails, signs remain clearly visible.

Who is responsible for maintaining fire exits?
The Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order (RRFSO) 2005 charges the Responsible Person in control of non-domestic premises with the safety of everyone on site, including employees, visitors, and contractors.
Under Article 14 of the RRFSO, this duty of care includes ensuring that “routes to emergency exits from premises and the exits themselves are kept clear at all times” (14: 1). These “emergency routes and exits must lead as directly as possible to a place of safety” (14: 2: a).
This means that the Responsible Person must ensure that the entire escape route, remain unobstructed at all times. ‘The entire escape route” includes outdoor routes from the final exit of a building to a place of safety. To achieve this, staff should be educated educating staff on the importance of good housekeeping for fire safety. This encourages the whole team to maintain clear exit routes.
What type of door is on a fire escape route?
Fire doors are doors with a certified fire rating, meaning that they have been tested to withstand fire for a set period of time (usually 30 or 60 minutes). Fire doors halt the spread of flames and smoke for this time, slowing the spread of fire throughout the building. This is called ‘compartmentation’, which provides time for building users to evacuate. Further to this, compartmentation limits damage to the building before emergency services can get the fire under control.
In most cases, the final exit door, which leads to the outside, is not a fire rated door. Doors along the escape route, however, usually need to be certified fire doors. That is because these doors are involved in compartmentation of the building.
For more information on the differences between fire exit and fire doors, visit our blog.
Can a fire exit be locked?
Fire exit doors must provide building users with immediate access to the outside of the building. This means that they cannot be locked internally. Instead, fire exits must be fitted with appropriate ‘panic hardware’ (push pads or panic bars) to enable rapid escape.
To prevent misuse of fire exit doors in non-emergency situations, tamper seals or security alarms can be fitted. Alarms will sound upon opening of the door, which notifies security of a breach. Tamper seals snap easily, so the door will open in an emergency. When installed, they to discourage misuse, while ‘tracking’ unauthorised entry/exit from the building. If the tamper seal is broken, the door has been used, which can be logged. These products are, of course, only suitable for doors which are for emergency use only, and do not serve as access doors in normal circumstances.
These mechanisms can be fitted with outside access devices, so that the door cannot be opened from the outside. This prevents unauthorised access, while maintaining an effective fire exit.

Holding fire exits open
Fire doors, involved in compartmentation, should never be held open without a fire door retainer. However, it is permitted to hold open a fire exit, either to improve accessibility or ventilation.
A ‘hold-back’ device can be fitted on panic and emergency exit operating mechanisms, enabling fire exit doors to be held open.
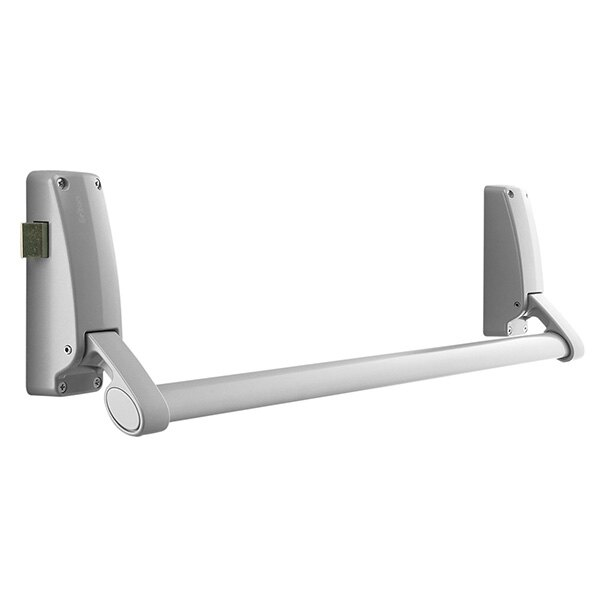
What are panic bars?
Panic bars are designed for use by visitors to public premises, who are not familiar with the building. In these circumstances, a ‘panic’ situation could easily arise if the fire alarm sounds and people have suddenly to evacuate.
A panic bar will open the fire exit even when people are pressed tightly against the bar and door. In a panic situation, this is useful when dense crowding causes people to eb unable to move their hands. All final escape doors that could be used by members of the public during an escape are therefore categorised as ‘panic exit doors’. These must be fitted with escape hardware that has been certified to BS EN1125.
In order to open fire exit doors, fitted with panic hardware, from the outside, an appropriate outside access device will have to be fitted: for example, a knob or lever operated unit with either a cylinder lock and key or a heavy duty keypad lock. This secures the fire exit against unauthorised access.
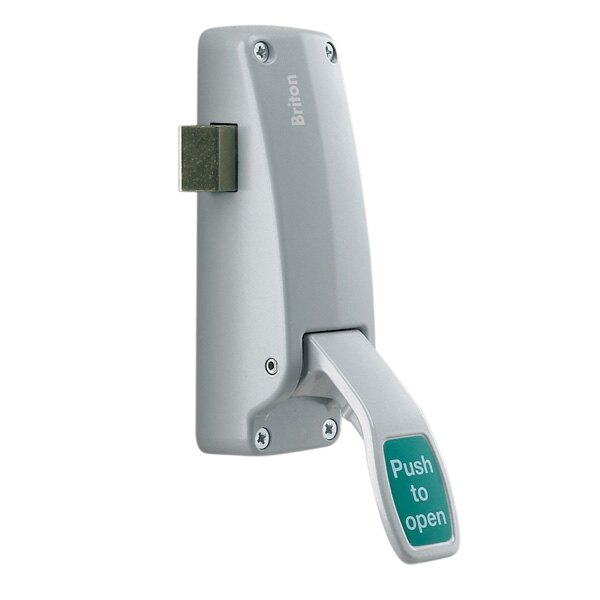
What are emergency push pads
Emergency push pads are designed for use on the final exit on an escape route in commercial premises, like offices. These pads are smaller than panic bars, so they require more precision for activation. Staff in commercial premises should be familiar with the building layout, and have appropriate training with regular fire drills. This training ensures that staff do not panic in an emergency, and can safely operate the push pad.
Fire safety guidelines set out by the former DCLG, now the Department for Levelling Up, Housing, and Communities, state that “premises with limited numbers of staff or others who are familiar with the building and where panic is not likely may use alternative devices (to panic bars), for example push pads or lever handles”. All final exit doors that are used only by trained personnel are categorised as ’emergency exit doors’. These must be fitted with emergency exit hardware certified to BS EN179.
Outside access devices for use with push pads include knob or lever operated units with cylinder or keypad locks.
Bolts vs latches on panic hardware
Latch fastening is suitable for use on single doors or the active leaf (i.e. the first opening leaf) of rebated double doors. When the panic bar or push pad is pressed, the latch retracts, releasing the door.
Bolt fastening features a vertical bolt that secures the door at the top and bottom. When the panic bar or push pad is pressed, the bolt retracts simultaneously from top and bottom to release the door. If an attempt is made to force the door from outside, for example by levering the bottom bolt out of position, the top bolt will remain in situ, and vice versa. This security feature is known as “two-point independent locking”. Non-rebated double doors should be secured with double bolts.
Single vertical bolts are suitable for use on single doors and the inactive (i.e. second opening leaf) of rebated double doors. In the latter case, pressing the panic bar on the inactive leaf and pushing against the door will also cause the active leaf to open.
Both types of mechanism can be fitted with an external locking system for security purposes.
Maintenance of panic/emergency exit hardware
Regular testing of panic and emergency exit hardware is essential for the maintenance of escape routes. Points to check and address as necessary include:
- Exit device function
- Component condition
- Security of fixings
In addition, the exit itself must always be kept clear of any obstruction that would hinder the function of exit hardware or the escape of people from the building.
What is the minimum width for fire escapes?
New and structurally altered buildings
Corridors in new buildings or building extensions which are part of a fire escape route must be at least 1200mm (1.2m) wide along the full length. If the width is less than 1800mm (1.8m), 1800 x 1800mm passing places should be integrated. This accounts for wheelchair accessibility.
Fire exit doors on these corridors should be no less than the width of the corridor minus 150mm. Therefore, a fire exit door on a corridor must be at least 1050mm. For fire exits from larger spaces, like sports halls, offices, and classrooms, a narrower doorway may be permitted, assuming the fire risk assessment deems it appropriate for the maximum capacity and expected use of that area of the building.
Existing buildings
In existing buildings, corridors should be at least 1000mm wide, or 1200mm if wheelchair accessibility is required. Fire exit doors in these premises are usually required to be at least 800mm wide.
How wide are fire exits required to be?
Further to the guidance on minimum widths, fire exits must be wide enough to ensure that all occupants can evacuate in an emergency. This calculation is based on the maximum number of occupants that each exit would be expected to serve in an emergency and the number of fire exits available, as well as the use of the building, and other specific risk factors on the premises.
If a storey or room has two or more exits, it should be assumed that a fire might prevent the occupants from using one of them. The remaining exit or exits therefore need to be wide enough to allow all the occupants to leave quickly. Therefore, when calculating the required widths of exits, it must be ensured that requirements can be met even if one of the exits is inaccessible.
Guidance for new buildings
Current building regulations contain guidance on the widths of escape routes and exits for new-build, non-domestic properties, and communal areas in purpose-built blocks of flats. “The Building Regulations 2010, Fire Safety, Approved Document B, Volume 2 – Buildings Other Than Dwellinghouses” provides guidance on how to calculate the required fire escape widths in a premises to comply with legislation. As a general rule, the minimum allowed fire exit door width is 750mm, but this depends on how many people are expected to use the exit, among other factors.
Guidance for existing buildings
The current BSI “Code of practice for fire safety in the design, management and use of buildings” (BS 9999: 2017) takes a complementary approach to this calculation. This approach is based on occupancy characteristics and fire growth rate. It is especially significant to escape routes and fire exits in existing premises, particularly if they are of a historical or heritage nature.
Combining these two factors creates the risk profile of a specific building. This means that in existing buildings, there is scope for an interpretative approach. Competent judgement on a case-by-case basis can therefore take into account the specific features of an individual building.
The ‘occupancy characteristic’ is determined according to whether the occupants are familiar or unfamiliar with the building, and whether they are likely to be awake or asleep. The Standard rates this risk from A (lowest) to C (highest) risk.
The fire growth rate is estimated according to the nature and quantity of combustible materials in a specific building. The standard rates this risk from 1 (lowest) to 5 (highest) risk.
Based on these characteristics, buildings are given a letter and number rating, from low (A1) to high (C3), which determines their level of risk. This ‘risk profile’ along with the building capacity can be used to calculate the required minimum width of fire exits.
How many fire exits are required?
The number of fire exits required depends upon the capacity and use of a building, as well as the width of the fire exits. For example, two double door fire exits may be more suitable than four single doors.
Government guidelines state that, if there is only one escape route, the travel distance should not be more than 18 metres. This reduces to 12 metres where there is a high risk of fire starting or spreading, but can be increased to around 25 metres in low-risk areas.
If there is more than one escape route, the travel distance should not exceed 45 metres; this reduces to 25 metres in high fire risk areas and can be increased to 60 metres where the risk is low.

Escape route and fire exit signage
In accordance with Article 14 (g) of the RRFSO, “emergency routes and exits must be indicated by signs”.
This is because an escape route will not necessarily be the route people would use under normal circumstances. In a fire situation, the travel distance to a place of safety must be as short as possible. Well-lit fire exit signs facilitate this by identifying the nearest escape route(s). The travel distance should be measured from the farthest point in a room to the door leading to a protected stairway or, if there is no protected stairway, to the final exit of the building.
BS 5499 and BS ISO EN 7010 compliant fire escape route signs affix easily to walls and are available in three sizes, with a viewing distance of 30 metres, 22 metres and 17 metres. The signs all show a man running through a rectangular doorway with a directional arrow pointing the way and may read “Fire exit” or “Exit”. Photoluminescent (glow-in-the-dark) versions of these signs are useful in areas of low visibility, accompanied by separate emergency lighting.
Illuminated Fire Exit Signs
Illuminated fire exit signs are recommended along escape routes in public places, where occupants are likely to be unfamiliar with their surroundings. Therefore, if the fire exit door requires a ‘panic bar’, fitting illuminated exit signage alongside separate emergency lighting is advised. These are battery powered (trickle charged from the mains electricity supply) and will light the escape route in the event of a power failure. They can be mounted on walls or ceilings, or suspended from chains where ceilings are high. Again, they show the man running, a directional arrow and a rectangular doorway, and may read “Fire Exit”.
Fire exit doors should also have appropriate signage, e.g. “Fire Exit – Keep Clear”, with an illuminated fire exit sign above. The panic exit hardware must carry a “Push Bar to Open” sign. For emergency exits in commercial premises, each push pad must have a “Push” sticker where the pad needs to be pressed.
Helpful Links:
HM Government fire safety risk assessment guides
Door and Hardware Federation: Code of Practice Hardware for Fire and Escape Doors
The Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005
Fire Safety: Approved Document B
BS 9999:2017 – Fire safety in the design, management and use of buildings. Code of practice


