Wednesday 17th December 2014
 Smoke alarms have reduced the number of deaths and injuries related to fire in the UK dramatically over the last decades and are now an essential must-have in every household.
Smoke alarms have reduced the number of deaths and injuries related to fire in the UK dramatically over the last decades and are now an essential must-have in every household.
All these millions of smoke alarms, however, rely on batteries in one way or the other. Mains powered smoke alarms require a backup battery in case the mains power supply fails and battery powered smoke alarms use them, as the name suggests, as main source of power. When the battery comes to the end of its life the smoke alarm emits a regular beeping sound for several weeks before the battery finally expires. This gives the owner sufficient time to replace the battery.
As the voltage of a battery drops at lower temperatures, the first low battery warnings are usually emitted at night, when our houses are at the coolest, especially in autumn and winter. This can be very annoying as you are woken up in the middle of the night by a beep every 30 seconds. What can you do to avoid this? You should, of course, replace the batteries regularly before they are getting close to their expiry time and you should have spare batteries at home. However, when it comes to sealed longlife battery units, which last ten years. This situation is much harder to prepare for, as you cannot realistically have a set of complete smoke alarms in your drawer, just in case.
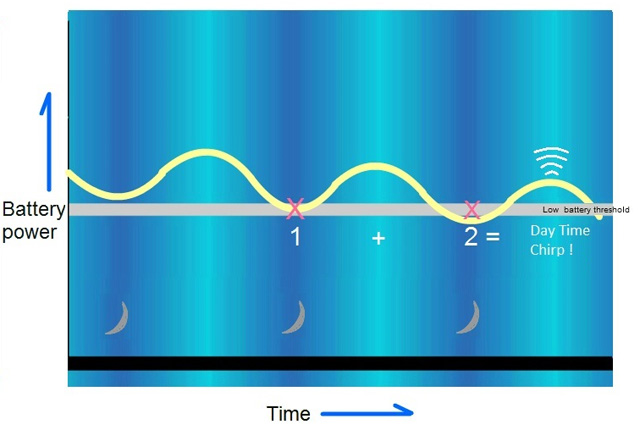
Kidde Fire Safety Products have come up with a brilliant concept to resolve this age old problem. Their longlife, sealed optical smoke alarm 10y29, which has a ten year lifespan, will detect the gradual weakening of its battery and then ensure that the alarm only starts beeping during daytime. This is achieved by monitoring the strengthening/weakening pattern of the battery voltage over a period of time as temperatures rise and fall during the day and nigh time. From this patterns the onboard chip of the smoke alarm will then define the day period and will only then raise the low battery alert during this time. An ingenious solution to a long standing problem.
Fig 1. Normal operation (showing the increasing and decreasing voltage pattern during daytime and night time)
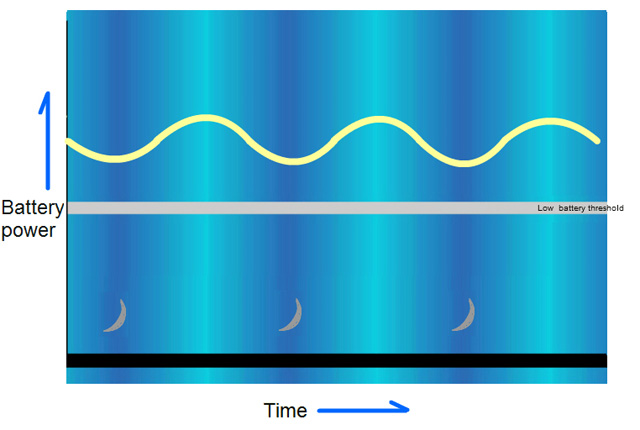
Fig 2. Dropping voltage and the response of traditional smoke alarms which start beeping in the night
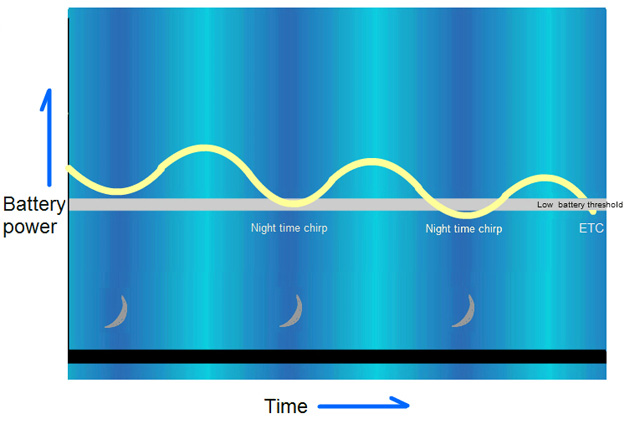
Fig 3. Kidde’s 10y29 smoke alarm, which records the night time lows but only starts beeping in the daytime